Why can ESD plastic trays protect electronic products?
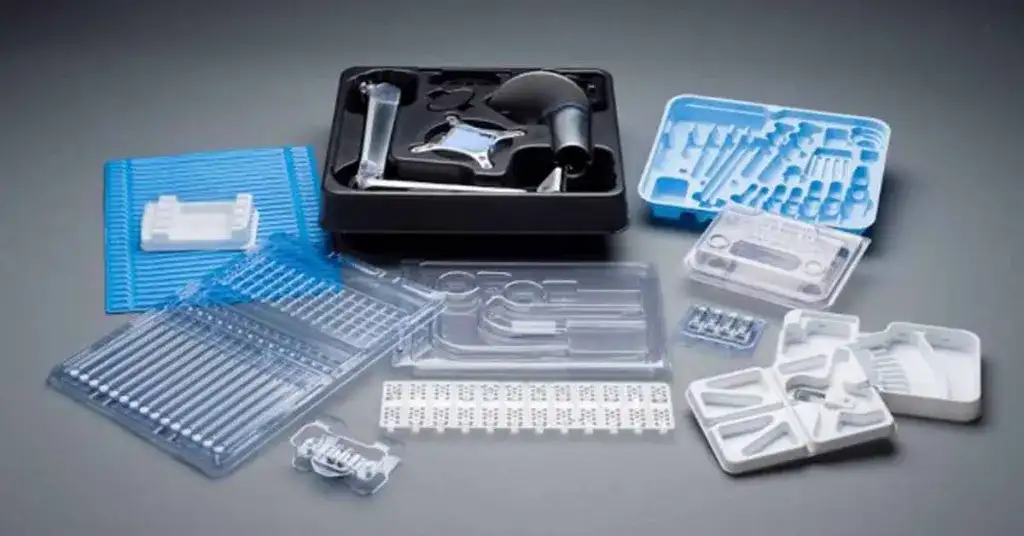
Reasons of ESD plastic trays to protect electronic products
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) plastic trays are designed to protect electronic products from the harmful effects of static electricity. Here’s how they achieve this:
1. Static Dissipation: ESD plastic trays are made from materials that have conductive or dissipative properties. These materials allow static electricity to be safely discharged away from sensitive electronic components. This prevents the accumulation of static charges which can otherwise cause damage to electronic circuits.
2. Preventing Static Generation: The materials used in ESD plastic trays are engineered to minimize the generation of static electricity. This is achieved through the use of anti-static additives that reduce the surface resistivity of the plastic, making it less likely for static charges to build up in the first place.
3. Shielding from External ESD Events: Some ESD plastic trays are designed to provide shielding against external electrostatic discharge events. These trays can have a conductive outer layer that redirects ESD away from the sensitive electronic components inside.
4. Maintaining Controlled Environment: By using ESD plastic trays, a controlled environment can be maintained during the handling, transportation, and storage of electronic components. This ensures that the components are consistently protected from static electricity.
5. Compliance with Industry Standards: ESD plastic trays are manufactured to meet specific industry standards and guidelines for ESD protection. These standards ensure that the trays provide an adequate level of protection for various types of electronic components.
ESD plastic trays are essential in the electronics industry to safeguard sensitive components from the potentially destructive effects of static electricity.
Model and type of ESD plastic tray to protect electronic products
1. Standard Anti-Static Trays
ESD Euro Stackable Container: These trays comply with European standards and are typically used for storing and transporting electronic components and subassemblies.
ESD Injection Molded Trays: Manufactured using injection molding, these trays have a smooth surface and are suitable for storing precision electronic products.
2. PCB Specific Trays
PCB Racks and Trays: Specifically designed for storing and transporting printed circuit boards (PCBs), these trays feature dedicated slots or fixed positions to prevent PCB movement.
Conductive PCB Transport Boxes: Used to protect and transport PCBs, these boxes offer good anti-static performance and structural strength.
3. Component Anti-Static Trays
Component Storage Trays: Suitable for storing and organizing small electronic components, typically featuring multiple compartments for easy organization.
IC Shipping Trays: Used for transporting integrated circuits (ICs) and chips, providing individual isolation and anti-static protection.
4. Hard Drive and Storage Device Trays
Hard Drive Carriers: Specifically designed for transporting and storing hard drives and SSDs, offering anti-static and shock-resistant protection.
ESD Protective Bins: Suitable for storing and protecting various storage devices and related accessories.
5. Tool and Instrument Trays
ESD Tool Trays: Used to store and organize anti-static tools and instruments, often equipped with custom grooves and compartments.
ESD Workstation Trays: Used in workstations for storing and organizing anti-static tools and small equipment.
6. Custom Trays
Custom ESD Trays: Tailored to meet specific size and shape requirements of electronic products, providing optimal protection.
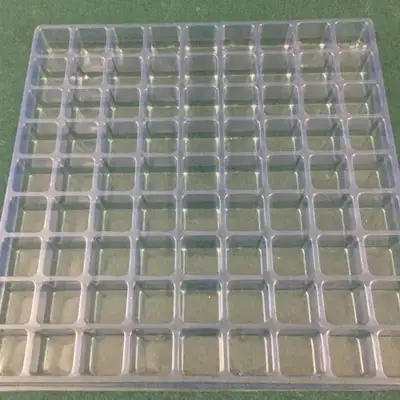


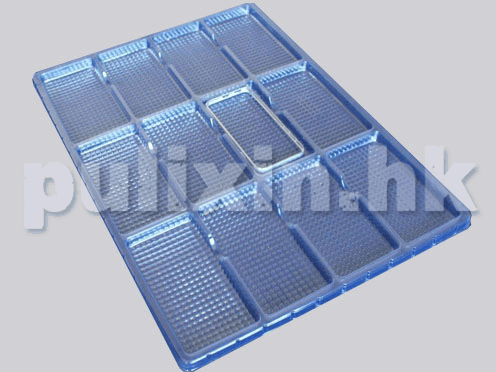



These trays serve various purposes in protecting electronic components and devices from electrostatic discharge (ESD) during storage, transportation, and handling processes.
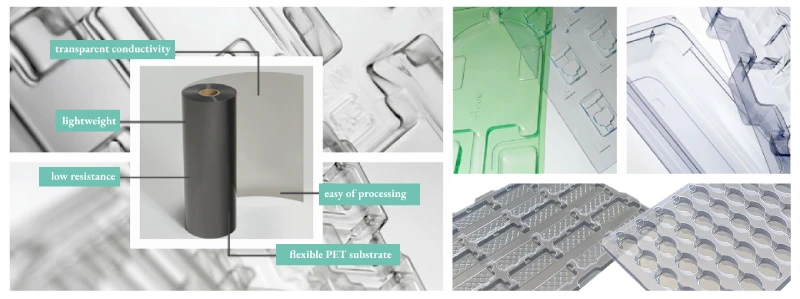
Make plastic sheet rolls for ESD plastic trays to protect electronic products
Materials suitable for making ESD plastic trays to protect electronic products often require good conductivity and mechanical strength. Here are some common types of plastic sheet rolls suitable for making anti-static trays:
1. PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): PET material, after ESD treatment, exhibits good anti-static performance and transparency. It has excellent physical properties and is easy to process into various tray shapes.
2. HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene): HIPS material can also achieve anti-static effects through the addition of conductive fillers. It is cost-effective, easy to mold and process, and suitable for making trays of various sizes.
3. PP (Polypropylene): PP material itself is not conductive, but it can achieve anti-static properties by adding conductive fillers. It has excellent chemical stability and durability, making it suitable for long-term storage and transportation.
4. PS (Polystyrene): PS material can also be made anti-static by adding conductive fillers under specific conditions, used for making relatively simple anti-static trays. It is cost-effective and suitable for economical applications.
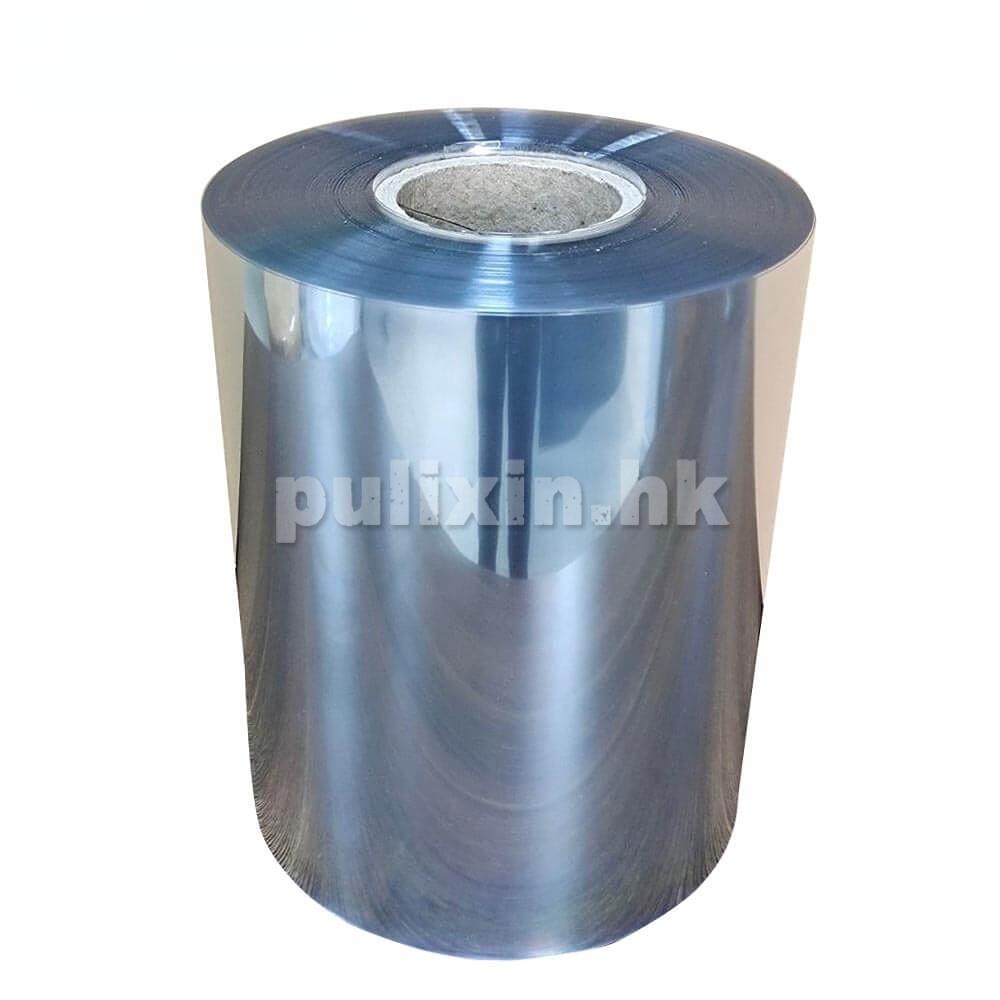
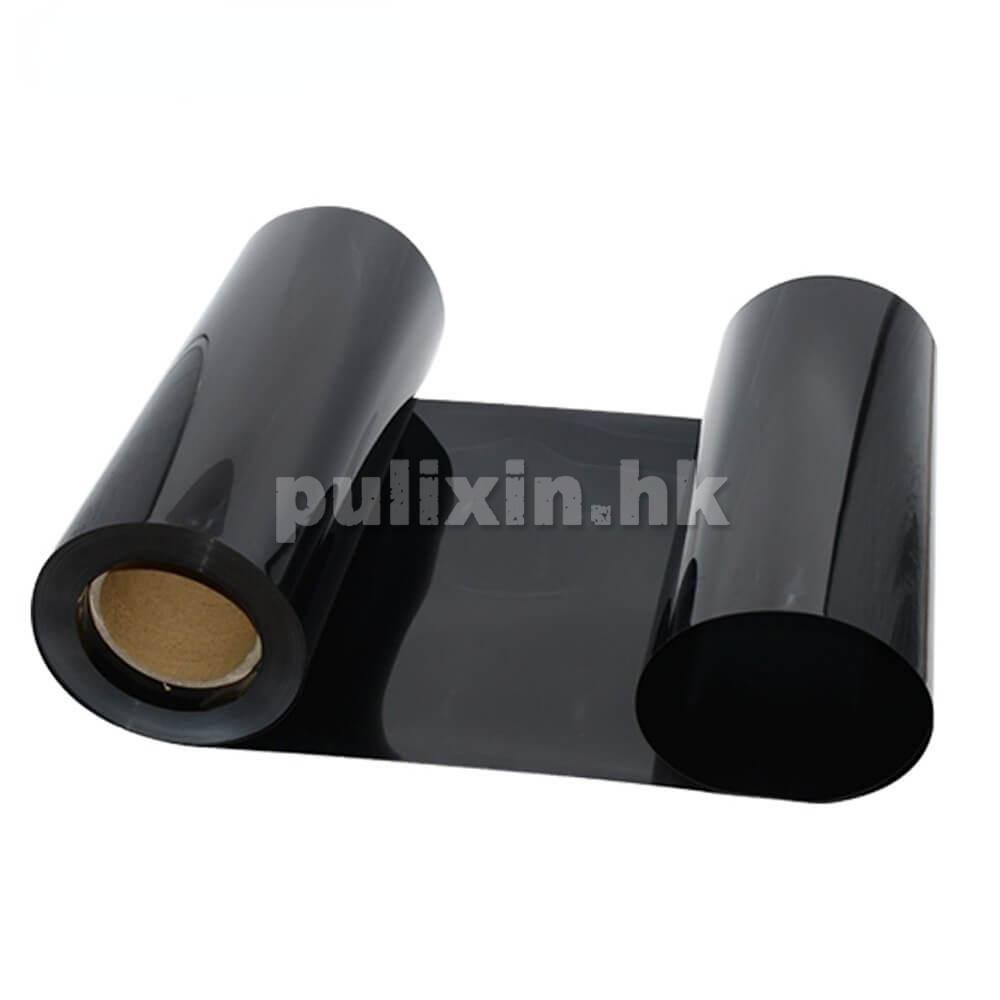




These materials are chosen based on their ability to effectively dissipate static electricity and provide robust physical protection for electronic components during storage and transport.
Pick of ESD plastic trays to protect electronic products
When selecting an ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) plastic pallet to safeguard electronic products, it's crucial to consider the following key factors:
1. ESD Protection Level: Ensure the pallet provides adequate ESD protection, typically measured in ohms. Lower resistance (measured in ohms) indicates better ESD protection. Look for pallets with a surface resistance within the acceptable range for your specific electronic products.
2. Material Composition: The type of plastic used in the pallet can affect its ESD properties. Materials like conductive or static dissipative plastics are designed to safely dissipate static charges, thereby protecting sensitive electronic components. Conductive materials typically have lower resistance levels compared to static dissipative ones.
3. Surface Characteristics: The surface of the pallet should be smooth and free of contaminants that could potentially generate static charges or damage electronic components.
4. Load Capacity: Consider the weight and size of the electronic products that will be placed on the pallet. Ensure the pallet can adequately support the load without compromising its ESD protection capabilities.
5. Durability and Longevity: Evaluate the pallet's durability, especially if it will be used in a warehouse or manufacturing environment where it might encounter frequent handling and transportation.
6. Compatibility with Handling Equipment: Ensure the pallet is compatible with your existing handling equipment such as forklifts and pallet jacks. This includes considerations like size, shape, and weight.
7. Cleanliness and Ease of Maintenance: Opt for pallets that are easy to clean and maintain to prevent contamination and ensure consistent ESD performance over time.
8. Regulatory Compliance: Check if the pallet meets relevant industry standards and regulations for ESD protection to ensure it will effectively safeguard your electronic products.


By carefully considering these factors, you can select an ESD plastic pallet that provides reliable protection for your electronic products throughout the storage and transportation stages. Pulixin(Hongkong) Packaging Material is your trusted partner.

